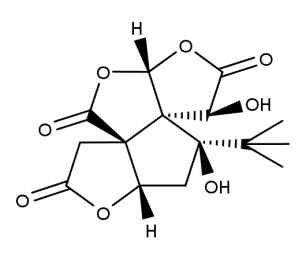
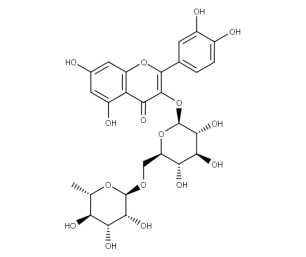
- Code : #3815 S 10 mg
- Formula : C₁₅H₁₈O₈
- CAS : 33570-04-6
Ginkgo biloba
Ginkgo biloba, “Maidenhair tree” in English, “Arbre aux quarante écus” in French, belongs to the Ginkgoaceae botanical family and is the only living species in the order Ginkgoales.
Native to northern China, it is a tree to 40 m tall, naturally scattered in broad-leaved forests and valleys but now a rare species in the wild.
It is sacred to Buddhists and often planted near temples. It tolerates a wide range of climatic and edaphic conditions.
The seeds are edible, and the leaves have a long history of medicinal use in traditional Chinese medicine. Research has shown that they stimulate blood circulation, reduce lethargy, treat asthma, eye and hearing disorders. Improving memory, they have been prescribed for Alzheimer disease and cognitive deficit. The fruit also has many active components.
The leaves’ main compounds are flavone glycosides (quercetin, kaempferol and isorhamnetin glycosides), terpene lactones (ginkgolides and bilobalide); several acids, proanthocyanidines, glucose, rhamnose etc.

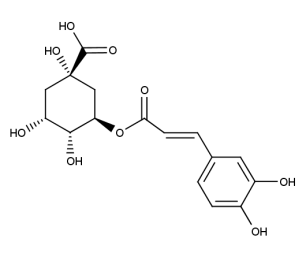
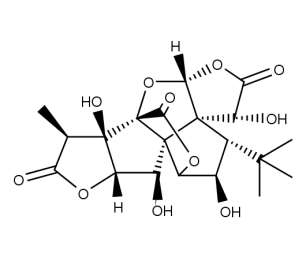
- Code : #4991 S 50 mg
- Formula : C₁₆H₁₈O₉
- CAS : 327-97-9
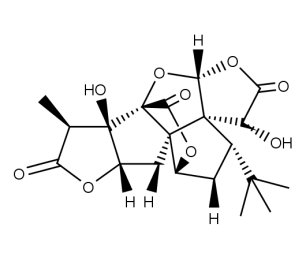
- Code : #3728 S 10 mg
- Formula : C₂₀H₂₄O₉
- CAS : 15291-75-5
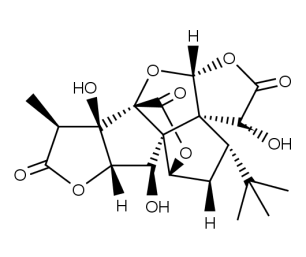
- Code : #3729 S 10 mg
- Formula : C₂₀H₂₄O₁₀
- CAS : 15291-77-7
- Code : #3730 S 10 mg
- Formula : C₂₀H₂₄O₁₁
- CAS : 15291-76-6
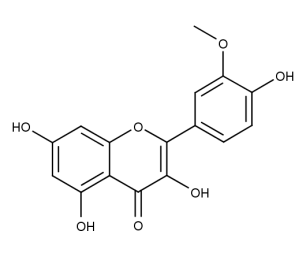
- Code : #1120 S 20 mg
- Formula : C₁₆H₁₂O₇
- CAS : 480-19-3
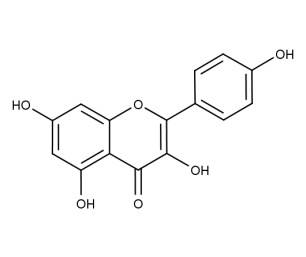
- Code : #1124 S 20 mg
- Formula : C₁₅H₁₀O₆
- CAS : 520-18-3
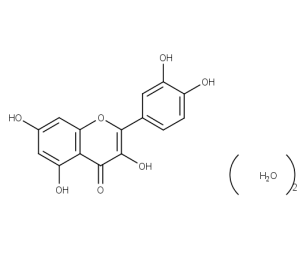
- Code : #1135 S 20 mg
- Formula : C₁₅H₁₀O₇,2H₂O
- CAS : 6151-25-3
- Code : #1139 S 50 mg
- Formula : C₂₇H₃₀O₁₆
- CAS : 153-18-4