- Code : #0573 S 20 mg
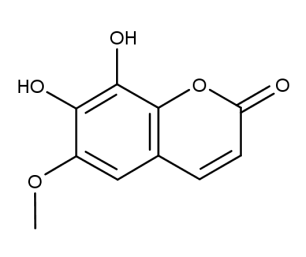
- Formula : C₁₀H₈O₅
- CAS : 574-84-5
Fraxinus excelsior
Fraxinus excelsior, “Ash” in English and “Frêne” in French, belongs to the Oleaceae botanical family. Native to Europe, North Africa and West Asia, it is a tree that grows to 18 m tall, sometimes 30 m or more.
Widely used for its timber, European ash produces wood that is both strong and elastic.
In traditional medicine, its bark was used to treat fevers and its sap as a remedy for earache and warts. The leaves are used to treat diarrhoea, dysentery, jaundice, joint pain, malaria, sores, swelling and wounds. They are astringent, cathartic, diaphoretic, mildly diuretic, laxative and purgative.
Among its main constituents are (Z,Z,Z)-n-tetratriacont-3,5,15-triene, n-hexatriacontane, (Z,Z,Z)-n-octatriacont-11,13,20-triene, phytanic acid (3,7,11,15-tetramethylhexadecanoic acid, 26-hydroxystigmasterol-18-oic acid and α-L-xylose. Also iridoids like nuzhenide and GL3 and coumarins like fraxetin and fraxin.

- Code : #0525 10 mg
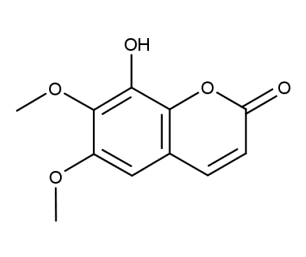
- Formula : C₁₁H₁₀O₅
- CAS : 525-21-3
- Code : #0588 S 10 mg
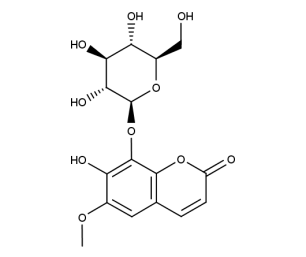
- Formula : C₁₆H₁₈O₁₀
- CAS : 524-30-1
- Code : #B9032 5 g
- Code : #0237 50 mg
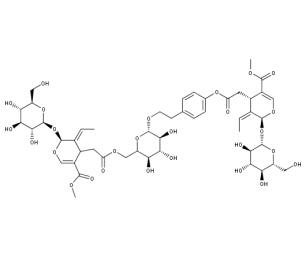
- Formula : C₄₈H₆₄O₂₇
- CAS : 60037-39-0
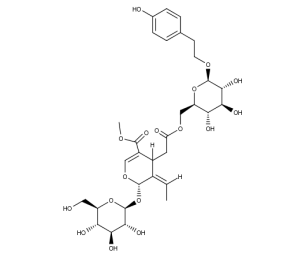
- Code : #0238 10 mg
- Formula : C₃₁H₄₂O₁₇
- CAS : 39011-92-2
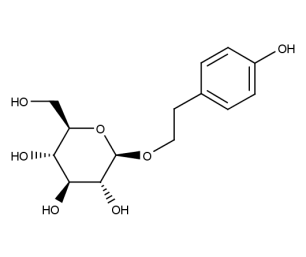
- Code : #4943 S 10 mg
- Formula : C₁₄H₂₀O₇
- CAS : 10338-51-9