- Code : #6034 S 20 mg
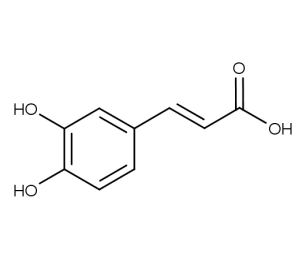
- Formula : C₉H₈O₄
- CAS : 331-39-5
Echinacea pallida
Echinacea pallida, “Pale purple coneflower” in English, called “Echinacée pâle” in French, belongs to the Asteraceae botanical family.
This herb is native to North America where it grows in rocky prairies, open wooded hillsides and glades. It is cultivated in Europe to some extent.
It is mainly the root that is used to make the drug, which comes from the traditional medicine of North America’s native Indians. Along with Echinacea purpurea and Echinacea angustifolia, it was the most widely used plant drug in the US in the 19th century.
It is used as a medicine for the prophylaxis and treatment of colds and influenza, for the stimulation of immune defenses, and for its anti-infective, anti-viral and anti-fungal activity.
Its main constituents are echinacoside, cynarin, chicoric acid and chlorogenic acid.

- Code : #4987 S 10 mg
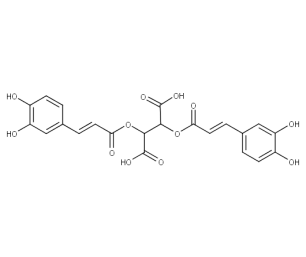
- Formula : C₂₂H₁₈O₁₂
- CAS : 70831-56-0
- Code : #4991 S 50 mg
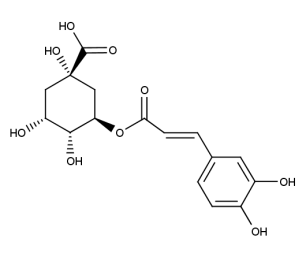
- Formula : C₁₆H₁₈O₉
- CAS : 327-97-9
- Code : #4995 S 10 mg
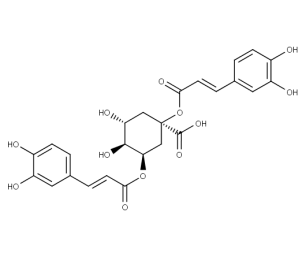
- Formula : C₂₅H₂₄O₁₂
- CAS : 30964-13-7
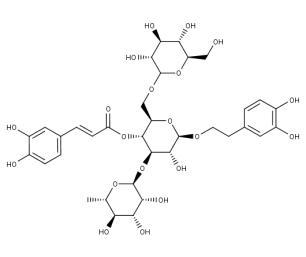
- Code : #4988 S 20 mg
- Formula : C₃₅H₄₆O₂₀
- CAS : 82854-37-3
- Code : #3532 S 10 mg
- Formula : C₂₉H₅₀O
- CAS : 83-46-5