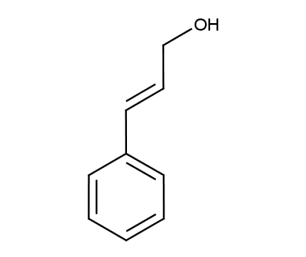
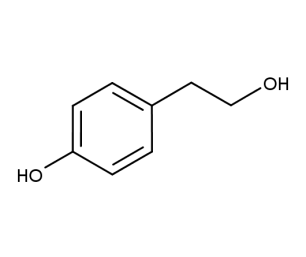
- Code : #6025 1 g
- Formula : C₉H₁₀O
- CAS : 104-54-1
Rhodiola rosea
Rhodiola rosea, synonym of Sedum roseum (L.) Scop., called “Roseroot” or “Arctic root” in English, “Rhodiole” or “Orpin rose” in French, belongs to the Crassulaceae botanical family. It is a herb growing to 0.3 m, native to boreal areas of Eastern Europe, European mountains, China and North America. In the Arctic, plants typically occur in crevices or among patches of moss and other vegetation, often near shores.
Rhodiola rosea has a long history of use as a medicinal plant for its dried roots and rhizomes, both in Asia and North America. Today, it is principally considered and used as an adaptogen.
Studies have revealed that Rhodiola preparations exhibit adaptogenic effect including, neuroprotective, cardioprotective, anti-fatigue, antidepressive, anxiolytic, nootropic, life-span increasing effects and Central Nervous System stimulating activity.
140 compounds were isolated from roots and rhizome - monoterpene alcohols and their glycosides, cyanogenic glycosides, aryl glycosides, phenylethanoids, tyrosol, salidroside, phenylpropanoids (coniferyl alcohol) and their glycosides, flavonoids, lignans, proanthocyanidins and gallic acid derivatives.

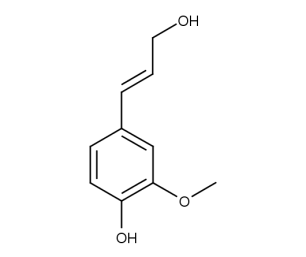
- Code : #4750 S 20 mg
- Formula : C₁₀H₁₂O₃
- CAS : 458-35-5
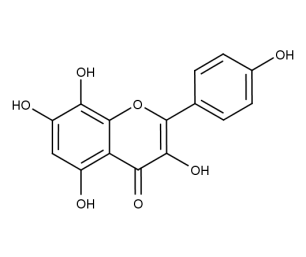
- Code : #1343 10 mg
- Formula : C₁₅H₁₀O₇
- CAS : 527-95-7
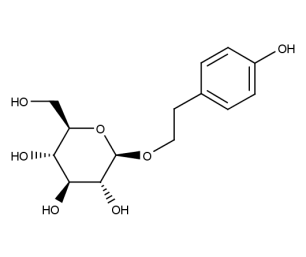
- Code : #4943 S 10 mg
- Formula : C₁₄H₂₀O₇
- CAS : 10338-51-9
- Code : #B0022 5 g
- Code : #4949 S 20 mg
- Formula : C₈H₁₀O₂
- CAS : 501-94-0