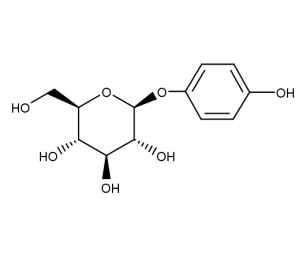
- Code : #0412 S 50 mg
- Formula : C₁₂H₁₆O₇
- CAS : 497-76-7
Verbena officinalis
Verbena officinalis, “Vervain” or “Common verbena” in English and “Verveine officinale” in French, belongs to the Verbenaceae botanical family.
Native to Europe, North Africa, and West Asia to the Himalayas, it is a herb growing to 0.6 m on waste grounds and roadsides.
The fragrant leaves are used to make tea, and in the food and cosmetics industries.
They have a long history as a drug both in European and Chinese medicinal traditions, being used as a diuretic, as an astringent for healing wounds and in fever, as a galactogogue, an expectorant in chronic bronchitis, and as an antirheumatic. Externally, it is used to treat minor injuries, eczema, sores, neuralgia and gum disease.
Among its main constituents are iridoid glucosides (verbenalin, hastatoside); caffeic-acid derivatives such as verbascoside; traces of essential oil, bitter substances and mucilage.

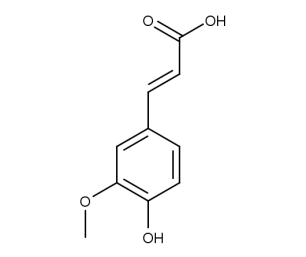
- Code : #4753 S 20 mg
- Formula : C₁₀H₁₀O₄
- CAS : 537-98-4
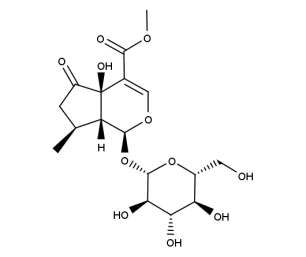
- Code : #0223 S 10 mg
- Formula : C₁₇H₂₄O₁₁
- CAS : 50816-24-5
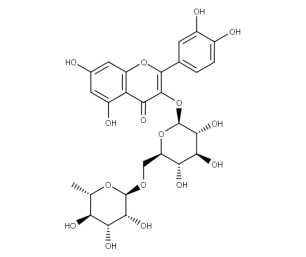
- Code : #1139 S 50 mg
- Formula : C₂₇H₃₀O₁₆
- CAS : 153-18-4
- Code : #B9098 5 g
- Code : #0239 S 10 mg
- Formula : C₁₇H₂₄O₁₀
- CAS : 548-37-8