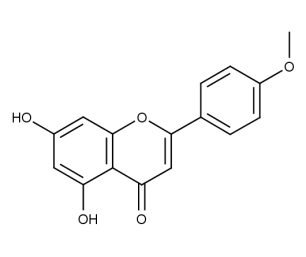
- Code : #1101 S 10 mg
- Formula : C₁₆H₁₂O₅
- CAS : 480-44-4
Valeriana officinalis
Valeriana officinalis, “Valerian” in English and “Valériane officinale” in French, belongs to the Valerianaceae botanical family. It is a herb that can reach 1.5 m.
Valeriana officinalis is native to Europe, where it is common except for the extreme south, and northern Asia; it was naturalized in North America. It grows in shady and wet meadows, forests and ditches, and along rivers.
Hippocrates described its properties, Galen later prescribed it as a remedy for insomnia, and both Europeans and Amerindians used it against epilepsy.
Its root is used as a sedative, and the isolated valepotriates are employed in some prepared medicines as psychostimulants.
The main constituents of its essential oil (0.3 to 0.7%) are bornyl acetate and other sesquiterpenes. Dried roots contain valepotriates (valtrate) and bicyclic iridoid monoterpenes. Valerenic and acetoxyvalerenic acid are characteristic constituents of the official drug.

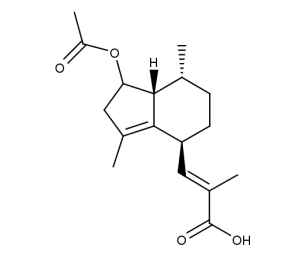
- Code : #3821 S 10 mg
- Formula : C₁₇H₂₄O₄
- CAS : 84638-55-1
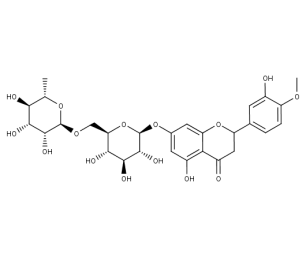
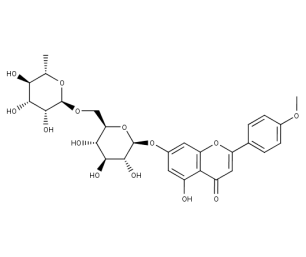
- Code : #1116 S 20 mg
- Formula : C₂₈H₃₄O₁₅
- CAS : 520-26-3
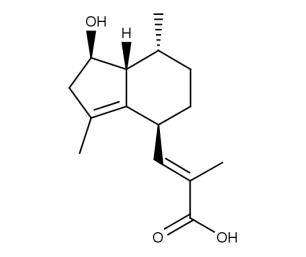
- Code : #3814 S 10 mg
- Formula : C₁₅H₂₂O₃
- CAS : 1619-16-5
- Code : #1169 S 10 mg
- Formula : C₂₈H₃₂O₁₄
- CAS : 480-36-4
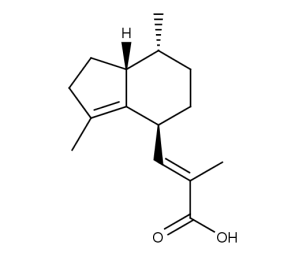
- Code : #3801 S 10 mg
- Formula : C₁₅H₂₂O₂
- CAS : 3569-10-6
- Code : #B9047 5 g
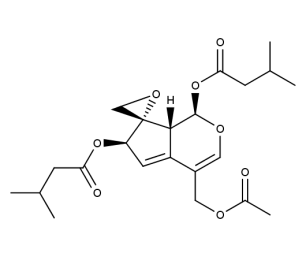
- Code : #0217 S 20 mg
- Formula : C₂₂H₃₀O₈
- CAS : 18296-44-1