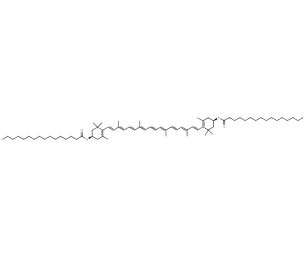
- Code : #0309 S 5 mg
- Formula : C₇₂H₁₁₆O₄
- CAS : 144-67-2
Lycium barbarum
Lycium barbarum, “Chinese wolfberry”, or “Chinese boxthorn” in English and “Lyciet commun” or “Lyciet de Barbarie” in French, belongs to the Solanaceae botanical family. Probably originating from South-East Europe to South-West Asia, maybe the Mediterranean basin, it is a shrub growing to 2.5 m that grows in hedges and waste grounds.
The fruit, goji berry, mainly used as a flavouring, is now being sold as health food in western countries, either dried or in juice.
Lycium barbarum has a long tradition of use in traditional Chinese medicine. The berries are used for blurry vision and diminished visual acuity, infertility, abdominal pain, dry cough, fatigue, and headache; to increase longevity and against prematurely gray hair. The root bark is used for night sweating, to treat cough, diabetes mellitus and hypertension.
The typical metabolites of the fruit are polysaccharides (arabinose, glucose, galactose, mannose, rhamnose, xylose, and/or galacturonic acid), carotenoids (mainly zeaxanthin dipalmitate), vitamins (riboflavin, thiamin and ascorbic acid) and flavonoids (myricetin, quercetin, and kaempferol).

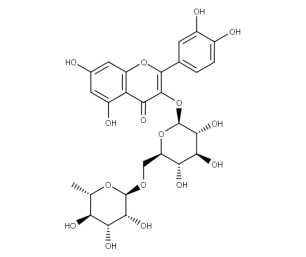
- Code : #1139 S 50 mg
- Formula : C₂₇H₃₀O₁₆
- CAS : 153-18-4
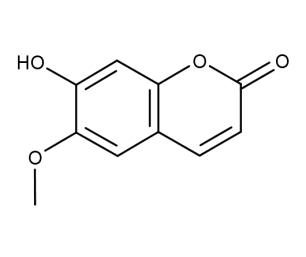
- Code : #0558 S 20 mg
- Formula : C₁₀H₈O₄
- CAS : 92-61-5
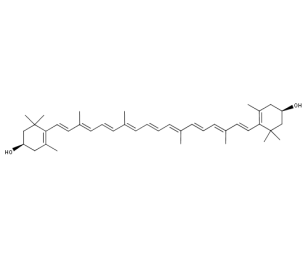
- Code : #0307 S 5 mg
- Formula : C₄₀H₅₆O₂
- CAS : 144-68-3