- Code : #0031 S 50 mg
- Formula : C₃₀H₄₈O₃
- CAS : 472-15-1
Chaenomeles speciosa
Chaenomeles speciosa, “Japanese quince” or “Flowering quince” in English, “Cognassier du Japon” or “Cognassier à fleurs” in French, belongs to the Rosaceae botanical family.
Native to East Asia, mainly several Chinese provinces, it is a thorny shrub to 3 m tall.
Once cooked, the fruit is used for jams and jellies, and as a flavoring with cooking apples.
The species has long been used in Traditional Chinese Medicine for rheumatism, cholera, dysentery, enteritis, beriberi and vitamin C deficiency syndrome.
Not only the leaves and fruits but various other parts of the plant including roots, seeds, bark twigs, and flowers all have long history of clinical trials in curing many human ailments.
In its composition enter a diversity of antioxidants, organic acids, phenolics, terpenoids, and many different phytochemicals that bear strong anticancer, antioxidant, antiviral, antibacterial properties, anti-inflammation, antihyperlipidemic, antihyperglycemic, and anti-Parkinson properties. It contains a series of chemical constituents, including triterpenoid (oleanolic acid), phenolic and phenylpropionic acids, flavonoids (hyperoside), saccharides, essential oils and alkaloids.

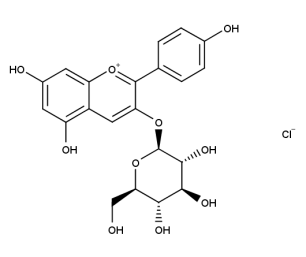
- Code : #0907 S 10 mg
- Formula : C₂₁H₂₁ClO₁₀
- CAS : 18466-51-8
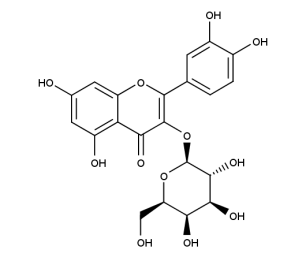
- Code : #1027 S 20 mg
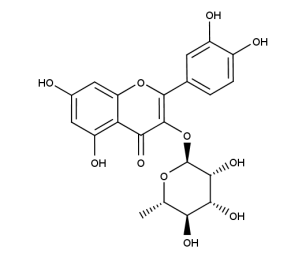
- Formula : C₂₁H₂₀O₁₂
- CAS : 482-36-0
- Code : #0923 S 5 mg
- Formula : C₂₁H₂₁O₁₁Cl
- CAS : 27661-36-5
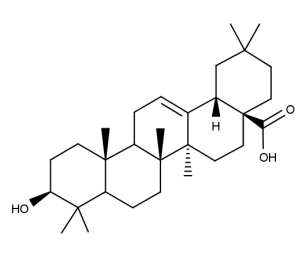
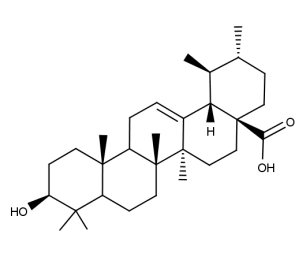
- Code : #0041 S 20 mg
- Formula : C₃₀H₄₈O₃
- CAS : 508-02-1
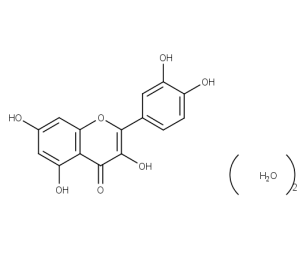
- Code : #1135 S 20 mg
- Formula : C₁₅H₁₀O₇,2H₂O
- CAS : 6151-25-3
- Code : #1236 S 20 mg
- Formula : C₂₁H₂₀O₁₁
- CAS : 522-12-3
- Code : #0037 S 20 mg
- Formula : C₃₀H₄₈O₃
- CAS : 77-52-1