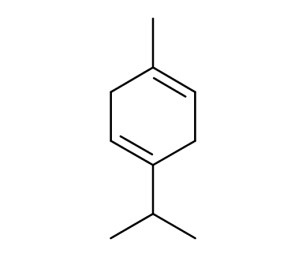
- Code : #5020 S 100 mg
- Formula : C₁₀H₁₄
- CAS : 99-87-6
Citrus reticulata
Citrus reticulata, « Mandarin orange » in English and « Mandarinier » in French, belongs to the Rutaceae botanical family.
Possibly native to south-east China and/or south Japan, it is a fruit tree 4 to 8m tall that grows at low elevations in hillside forests.
It is widely cultivated for its mandarin fruits, eaten raw or cooked in cakes etc. as well as the dried rind, used as a spice. In traditional Chinese medicine, the plant is used for the treatment of dyspepsia, gastro-intestinal distension, cough, hiccup and vomiting. The fruit have shown anti-inflammatory, anticholesterolemic, analgesic, antiasthmatic, antiscorbutic, antiseptic, antitussive, carminative, expectorant and stomachic activities.
The fruit’s main constituents are alkaloids, flavonoids, tannins, phenols and saponins. The rind’s main constituents are fat, protein, ash, magnesium, carotenoids, dietary fibre and polyphenols.

- Code : #5025 100 mg
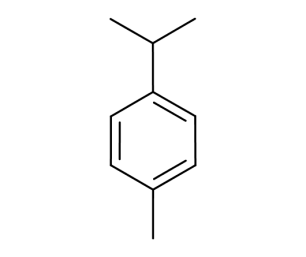
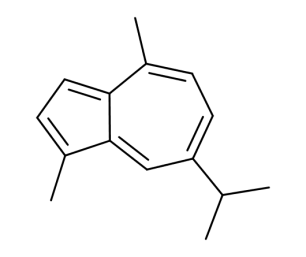
- Formula : C₁₅H₁₈
- CAS : 489-84-9
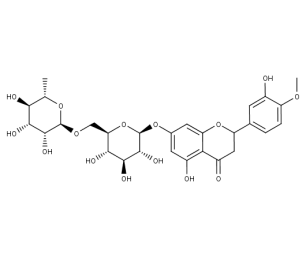
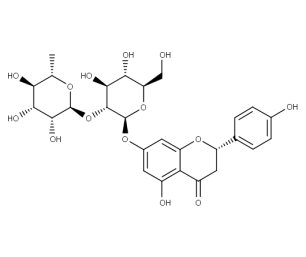
- Code : #1116 S 20 mg
- Formula : C₂₈H₃₄O₁₅
- CAS : 520-26-3
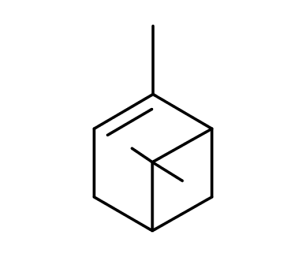
- Code : #5082 S 100 mg
- Formula : C₁₀H₁₆
- CAS : 5989-27-5
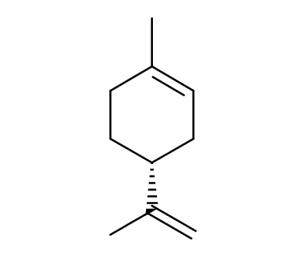
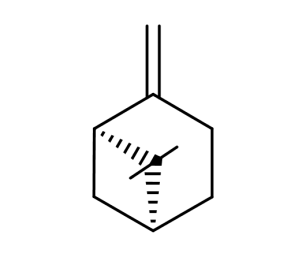
- Code : #5124 100 mg
- Formula : C₁₀H₁₆
- CAS : 123-35-3
- Code : #1129 S 20 mg
- Formula : C₂₇H₃₂O₁₄
- CAS : 10236-47-2
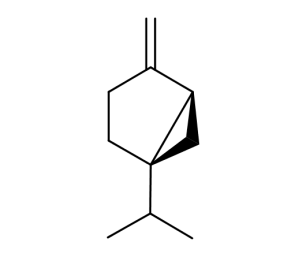
- Code : #5383 S 1 g
- Formula : C₁₀H₁₆
- CAS : 80-56-8
- Code : #5441 S 100 mg
- Formula : C₁₀H₁₆
- CAS : 18172-67-3
- Code : #5062 SA 100 mg
- Formula : C₁₀H₁₆
- CAS : 3387-41-5
- Code : #5065 S 100 mg
- Formula : C₁₀H₁₆
- CAS : 99-85-4
- Code : #5077 S 100 mg
- Formula : C₁₀H₁₈O
- CAS : 98-55-5