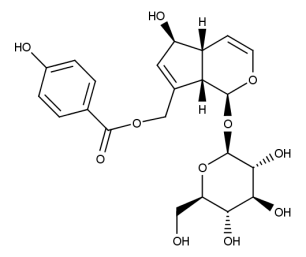
- Code : #0235 S 10 mg
- Formula : C₂₂H₂₆O₁₁
- CAS : 11027-63-7
Vitex negundo
Vitex negundo, “Chinese chaste tree” or “Five-leaved chaste tree” in English, “Muguet bleu” or “Troène de Chine” in French, belongs to the Lamiaceae botanical family.
Native to East Asia, it grows in wasteland up to 2000 m in the Himalayas and in mixed thickets on mountain slopes up to an altitude of 1400 m in China.
It is a shrub growing to 3 m by 3 m. Its seed is a pepper substitute and a tea is made from the roots and leaves.
Its fruit, root and leaves have been used to treat different conditions in Ayurvedic medicine as well as Roman medicine. It is credited with innumerable medicinal activities, and research has validated different therapeutic uses such as: antiandrogenic, anti-inflammatory, analgesic, hepatoprotective, anxiolytic etc.
Among its many chemical constituents, that vary according to the plant parts, are flavonoids, flavones glycosides, volatile oil, triterpenes, tannins and many others. Also vitexin, homoorientin, casticin, agnuside and negundoside.

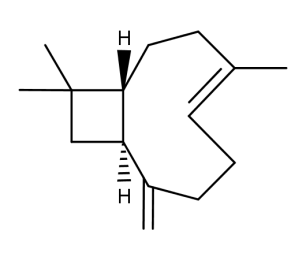
- Code : #5014 S 100 mg
- Formula : C₁₅H₂₄
- CAS : 87-44-5
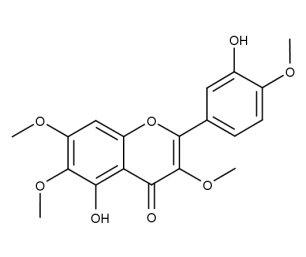
- Code : #1336 S 10 mg
- Formula : C₁₉H₁₈O₈
- CAS : 479-91-4
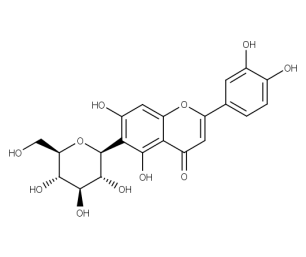
- Code : #1055 S 10 mg
- Formula : C₂₁H₂₀O₁₁
- CAS : 4261-42-1
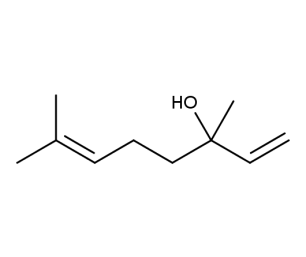
- Code : #5041 S 100 mg
- Formula : C₁₀H₁₈O
- CAS : 78-70-6
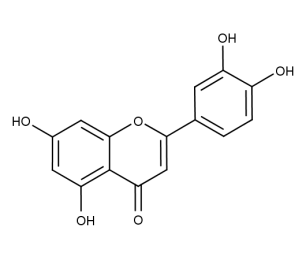
- Code : #1125 S 20 mg
- Formula : C₁₅H₁₀O₆
- CAS : 491-70-3
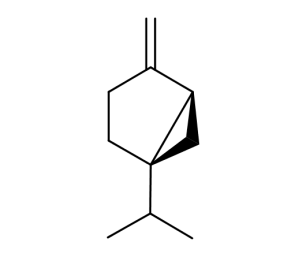
- Code : #5062 SA 100 mg
- Formula : C₁₀H₁₆
- CAS : 3387-41-5
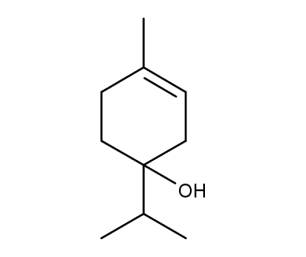
- Code : #5261 1 g
- Formula : C₁₀H₁₈O
- CAS : 562-74-3