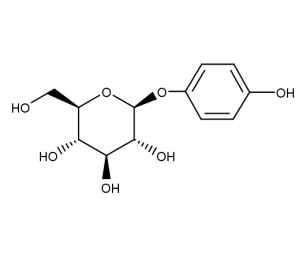
- Code : #0412 S 50 mg
- Formula : C₁₂H₁₆O₇
- CAS : 497-76-7
Urtica dioica
Urtica dioica, “Stinging nettle” in English and “Grande ortie” in French, belongs to the Urticaceae botanical family. Native to Europe, much of temperate Asia and western North Africa, it is a herb growing to 1.5 m tall on average in damp woods and waste areas.
Young plants are edible and stems contain a fiber that has been used to make clothing for 2000 years. Nettles are also used as a dye, as fodder, as a stimulant for plant growth etc.
In western folk medicine, aerial parts are used as a diuretic, for arthritis and rheumatism, biliary complaints, as an anti-diabetic, to help wound healing; externally, to treat seborrhea of the scalp. In traditional Chinese medicine, the root is used as a diuretic as well but, because of its tannin content, also as an astringent and gargle, and has been recommended in benign prostate conditions.
The main constituents of aerial parts are phenolic acids (5-O-caffeoylquinic acid as dominant) and flavonol glycosides (rutin, isoquercitrin, and kaempferol 3-O-glucoside). Lignans (secoisolariciresinol, 9,9′-bisacetyl-neo-olivil and their glucosides) are found in the root.

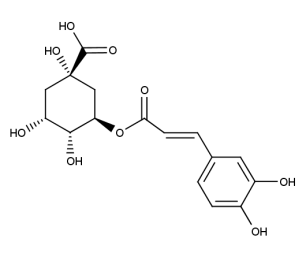
- Code : #4991 S 50 mg
- Formula : C₁₆H₁₈O₉
- CAS : 327-97-9
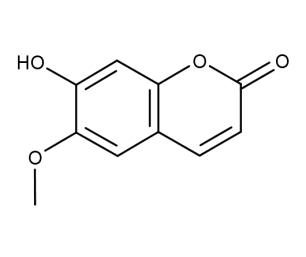
- Code : #0558 S 20 mg
- Formula : C₁₀H₈O₄
- CAS : 92-61-5
- Code : #3532 S 10 mg
- Formula : C₂₉H₅₀O
- CAS : 83-46-5
- Code : #B9160 5 g