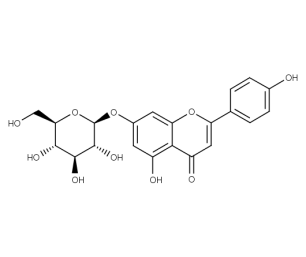
- Code : #1004 S 20 mg
- Formula : C₂₁H₂₀O₁₀
- CAS : 578-74-5
Salvia fruticosa
Salvia fruticosa, “Greek sage” or “Three-lobed sage” in English and “Sauge arbustive” ou “Sauge ligneuse” in French, belongs to the Lamiaceae botanical family. Native to Central and Eastern Mediterranean, it is a shrub growing to 1 m in dry rocky hillsides.
The leaves, illustrated in the House of Frescoes in Knossos, are used as tea, as a spice and as an adulterant of sage. In Greece, they are sometimes set on fire in a house to cleanse it.
As a drug, leaves are used in the treatment of digestive and respiratory complaints, menstrual problems, infertility, nervous tension and depression; against rheumatic pains, colds and influenza. Externally, as an antiseptic and for curing wounds, swellings and dropsy.
Among the main constituents of the plant are flavonoids, phenolic acids, fatty acids, mono-, sesqui-, di-and triterpenoids, steroids. It its essential oil, oxygenated monoterpenes are predominating with mostly 1,8-cineole and camphor.

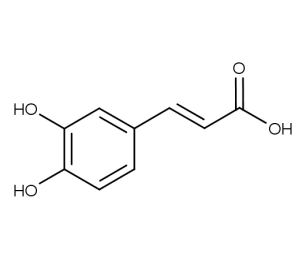
- Code : #6034 S 20 mg
- Formula : C₉H₈O₄
- CAS : 331-39-5
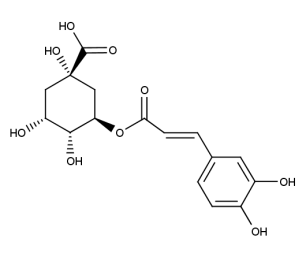
- Code : #4991 S 50 mg
- Formula : C₁₆H₁₈O₉
- CAS : 327-97-9
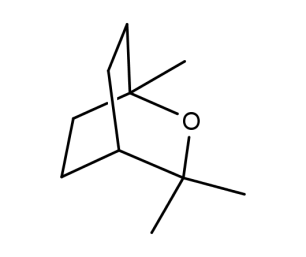
- Code : #5009 S 100 mg
- Formula : C₁₀H₁₈O
- CAS : 470-82-6
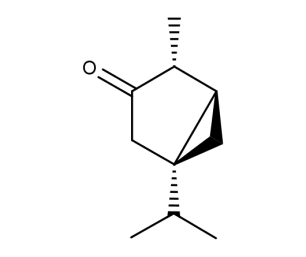
- Code : #5420 100 mg
- Formula : C₁₀H₁₆O
- CAS : 546-80-5