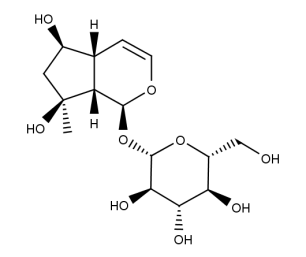
- Code : #0219 S 10 mg
- Formula : C₁₅H₂₄O₉
- CAS : 52949-83-4
Plantago lanceolata
Plantago lanceolata, “Ribwort plantain” or “Narrowleaf plantain” in English, “Plantain lancéolé” in French, belongs to the Plantaginaceae botanical family.
It is a herb, 10 to 40 cm tall, a common weed of meadows and fields, gardens and lawns, as well as wastelands, grassy paths, roadsides and cracks in pavement.
It is native to Europe and northern and central Asia.
As a medicine, Plantain herb is used to alleviate irritation in catarrh of the upper respiratory tracts and to treat inflammation of the mouth and throat. Its extracts have bacteriostatic and bactericidal activity and are applied externally in folk medicine as a wound-healing and inflammation-inhibiting remedy.
Its main constituents are iridoid glycosides including aucubin, catalpol and ajugol, and caffeic phenylethanoides, mainly verbascoside. Mucilage, with at least 4 polysaccharides; tannins, phenolic carboxylic acids and other acids; coumarin like esculetin, and flavonoids (apigenin).

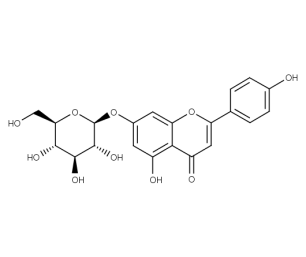
- Code : #1004 S 20 mg
- Formula : C₂₁H₂₀O₁₀
- CAS : 578-74-5
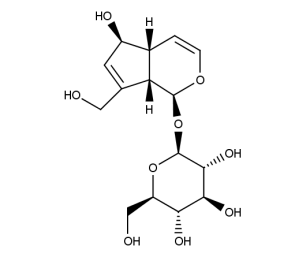
- Code : #0227 S 20 mg
- Formula : C₁₅H₂₂O₉
- CAS : 479-98-1
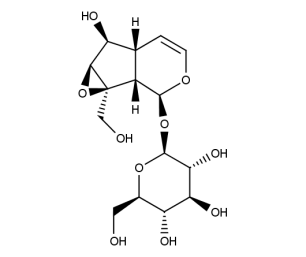
- Code : #0233 S 10 mg
- Formula : C₁₅H₂₂O₁₀
- CAS : 2415-24-9
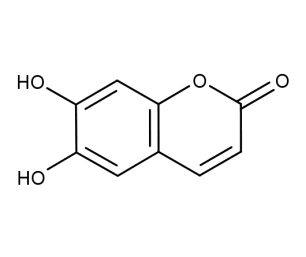
- Code : #0502 1 g
- Formula : C₉H₆O₄
- CAS : 305-01-1
- Code : #B9071 5 g
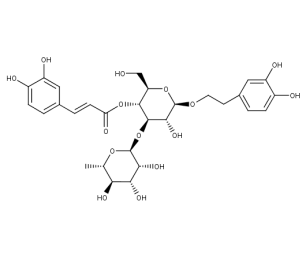
- Code : #4994 S 10 mg
- Formula : C₂₉H₃₆O₁₅
- CAS : 61276-17-3