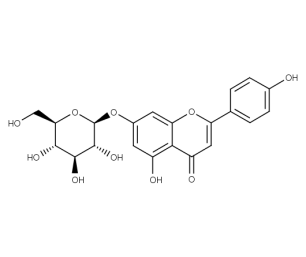
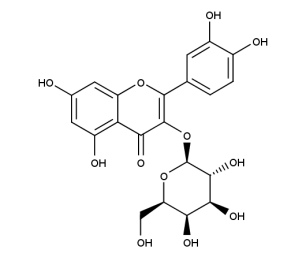
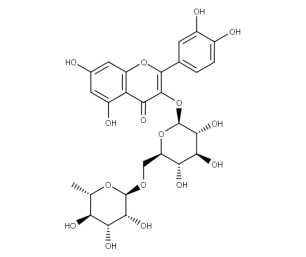
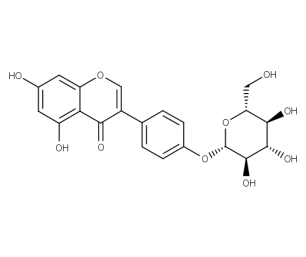
- Code : #1004 S 20 mg
- Formula : C₂₁H₂₀O₁₀
- CAS : 578-74-5
Styphnolobium japonicum
Styphnolobium japonicum, “Japanese pagoda tree” in English and “Sophora du Japon” or “Arbre à miel” in French, belongs to the Fabaceae botanical family. It is a tree growing to 25m in open country between 300 and 1000 m. Native to China, it was first described on cultivated specimen from Japan.
The wood, of superior quality, is used in carpentry. A yellow dye is obtained from the seedpods and the flowers.
Several plant parts have medicinal uses, but the flower buds are widely known in traditional Chinese medicine for treating dizziness, headache, hypertension, hematemesis, intestinal hemorrhage, and hemorrhoids.
Flower buds are constituted of many secondary metabolites like flavonoids, triterpenoids, and amino acids, but most of the pharmacological properties are attributed to both flavonoids and isoflavonoids. Rutin and quercetin are among the main constituents.

- Code : #1027 S 20 mg
- Formula : C₂₁H₂₀O₁₂
- CAS : 482-36-0
- Code : #1139 S 50 mg
- Formula : C₂₇H₃₀O₁₆
- CAS : 153-18-4
- Code : #1392 S 10 mg
- Formula : C₂₁H₂₀O₁₀
- CAS : 152-95-4