- Code : #4991 S 50 mg
- Formula : C₁₆H₁₈O₉
- CAS : 327-97-9
Fraxinus augustifolia
Fraxinus angustifolia, “Narrow-leaved ash” in English and “Frêne à feuilles étroites” in French, belongs to the Olaceae botanical family.
Native to Southern Europe, North Africa and West Asia, it is a tree that can reach a height of 25 m, growing in dryish rocky places in scrub or pine and mixed forest.
In Algerian folk medicine, different parts are used to treat many inflammatory diseases; leaves and fruits (samaras) are used in decoctions and infusions as anti-rheumatism, while bark is effective for curing hemorrhoids and fever. It is said to have diuretic and mild purgative effects as well as for the treatment of constipation, cystitis and itching scalp.
Its main constituents are flavonoids, coumarins (fraxin), iridoids and secoiridoids (nuzhenide); phenylethanoids, verbascoside, and three flavonoides glycosides : kaempferol 3-O-rutinoside, isoquercetrin (quercetin 3-O-glucoside) and rutin.

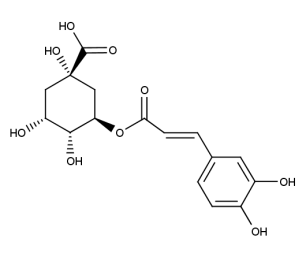
- Code : #0573 S 20 mg
- Formula : C₁₀H₈O₅
- CAS : 574-84-5
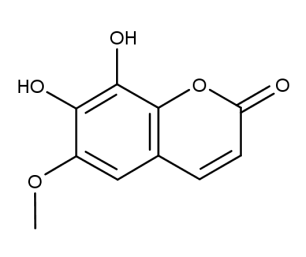
- Code : #0525 10 mg
- Formula : C₁₁H₁₀O₅
- CAS : 525-21-3
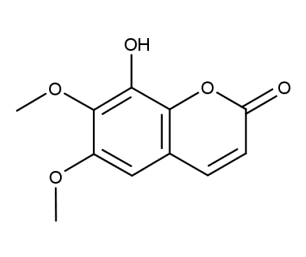
- Code : #0588 S 10 mg
- Formula : C₁₆H₁₈O₁₀
- CAS : 524-30-1
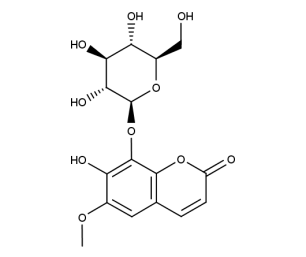
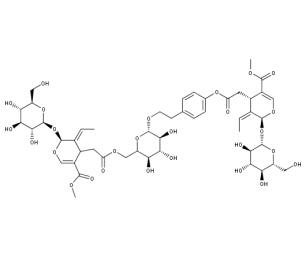
- Code : #0237 50 mg
- Formula : C₄₈H₆₄O₂₇
- CAS : 60037-39-0
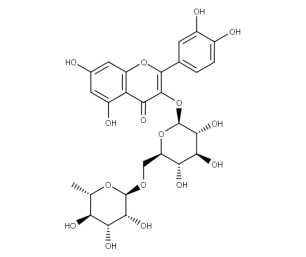
- Code : #1053 S 10 mg
- Formula : C₂₇H₃₀O₁₅
- CAS : 17650-84-9
- Code : #0238 10 mg
- Formula : C₃₁H₄₂O₁₇
- CAS : 39011-92-2
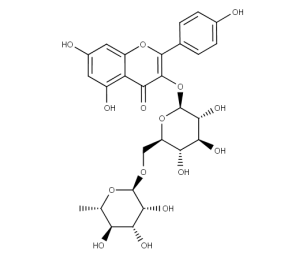
- Code : #1139 S 50 mg
- Formula : C₂₇H₃₀O₁₆
- CAS : 153-18-4
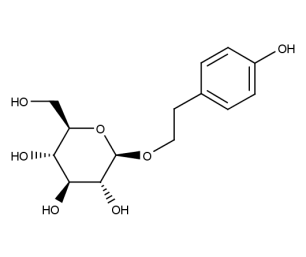
- Code : #4943 S 10 mg
- Formula : C₁₄H₂₀O₇
- CAS : 10338-51-9
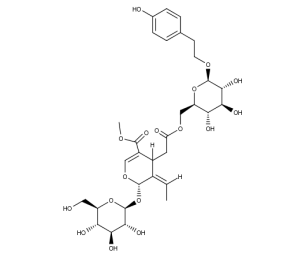
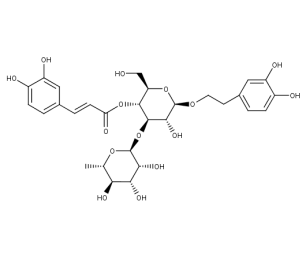
- Code : #4994 S 10 mg
- Formula : C₂₉H₃₆O₁₅
- CAS : 61276-17-3