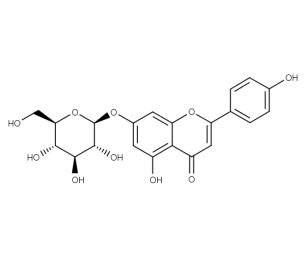
- Code : #1004 S 20 mg
- Formula : C₂₁H₂₀O₁₀
- CAS : 578-74-5
Olea europaea
Olea europaea, “Olive tree” in English and “Olivier” in French, belongs to the Olaceae botanical family.
Native to the Mediterranean region, Africa and Asia, it is a tree growing to 10 m that thrives in seasonally dry Mediterranean habitats or bushland vegetation in the tropic.
Commonly cultivated for its fruit, Olea europaea has grown for over 5000 years in the Mediterranean area where 95% of the production takes place. Olive oil is a key ingredient in cooking and has long been used in cosmetics, perfumes, and for medicinal purposes.
It is used traditionally as a diuretic, hypotensive, emollient, laxative, febrifuge, skin cleanser, cholagogue, and also for the treatment of urinary infections, gallstones, bronchial asthma and diarrhea.
Phytochemical research had led to the isolation of flavonoids, secoiridoids, mainly oleuropein, iridoids, hydroxytyrosol and tyrosol, flavones (luteolin), biphenols, triterpenes, benzoic acid derivatives, isochromanes, and other classes of secondary metabolites.

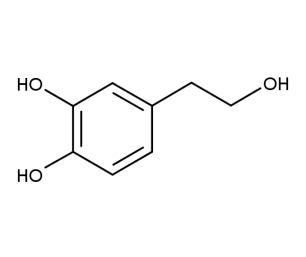
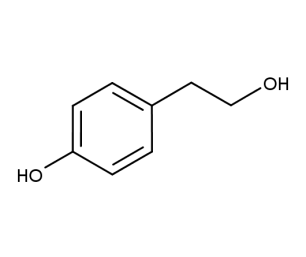
- Code : #4999 S 50 mg
- Formula : C₈H₁₀O₃
- CAS : 10597-60-1
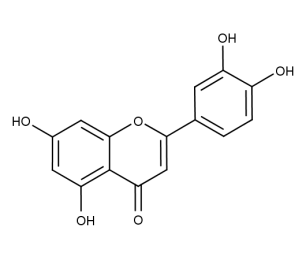
- Code : #1125 S 20 mg
- Formula : C₁₅H₁₀O₆
- CAS : 491-70-3
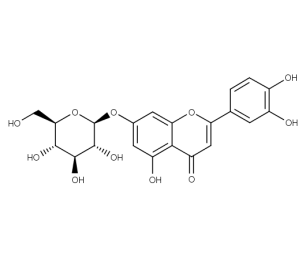
- Code : #1126 S 20 mg
- Formula : C₂₁H₂₀O₁₁
- CAS : 5373-11-5
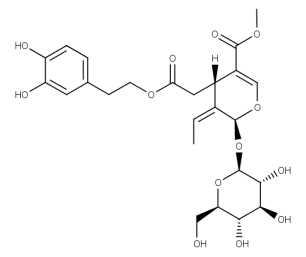
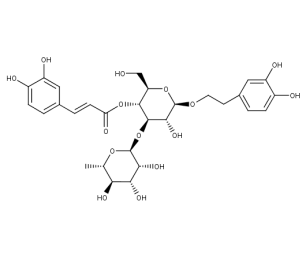
- Code : #0238 10 mg
- Formula : C₃₁H₄₂O₁₇
- CAS : 39011-92-2
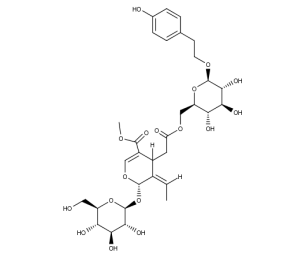
- Code : #0228 S 10 mg
- Formula : C₂₅H₃₂O₁₃
- CAS : 32619-42-4
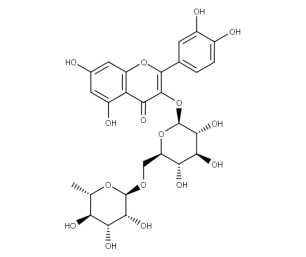
- Code : #1139 S 50 mg
- Formula : C₂₇H₃₀O₁₆
- CAS : 153-18-4
- Code : #4949 S 20 mg
- Formula : C₈H₁₀O₂
- CAS : 501-94-0
- Code : #4994 S 10 mg
- Formula : C₂₉H₃₆O₁₅
- CAS : 61276-17-3