- Code : #6034 S 20 mg
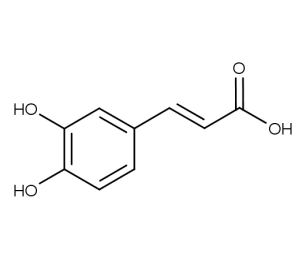
- Formula : C₉H₈O₄
- CAS : 331-39-5
Arnica montana
Arnica montana, “Wolf’s bane” or “Mountain arnica” in English and “Arnica des montagnes” in French, belongs to the Asteraceae botanical family.
It is a herb about 60 cm tall, native to Central Europe, growing in mountain pastures (especially in the Alps), pasture and open woodland.
Arnica has a long history of herbal use. All parts of the plant contain active compounds, but it is mostly the medicine made with its flower heads that is used as an external treatment for bruises and sprains. Homeopathic medicine recommends it for internal use to treat shock, injury and pain.
The constituents of Arnica montana vary according to the region but are mainly essential oils, fatty acids, thymol, pseudoguaianolide sesquiterpene lactones, mainly helenalin and flavanone glycosides (quercetin and kaempferol glucunorides)

- Code : #4991 S 50 mg
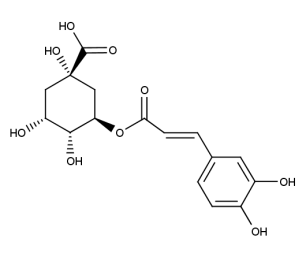
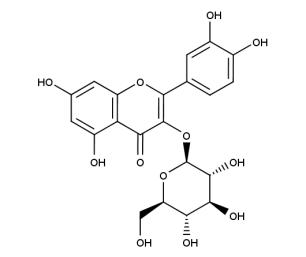
- Formula : C₁₆H₁₈O₉
- CAS : 327-97-9
- Code : #1243 S 10 mg
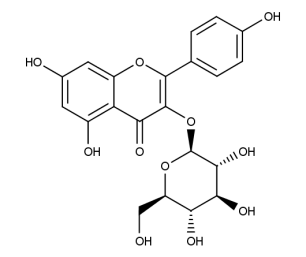
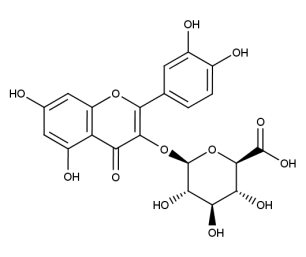
- Formula : C₂₁H₂₀O₁₁
- CAS : 480-10-4
- Code : #1356 S 5 mg
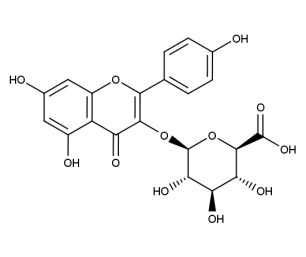
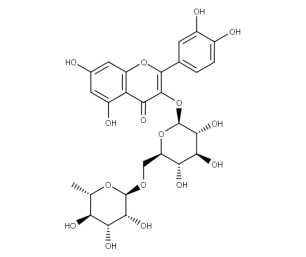
- Formula : C₂₁H₁₈O₁₂
- CAS : 22688-78-4
- Code : #1327 S 20 mg
- Formula : C₂₁H₂₀O₁₂
- CAS : 482-35-9
- Code : #1418 S 10 mg
- Formula : C₂₁H₁₈O₁₃
- CAS : 22688-79-5
- Code : #1139 S 50 mg
- Formula : C₂₇H₃₀O₁₆
- CAS : 153-18-4
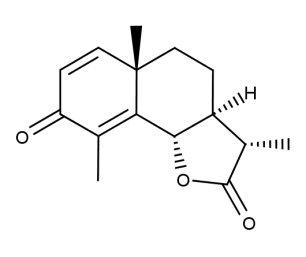
- Code : #6597 100 mg
- Formula : C₁₅H₁₈O₃
- CAS : 481-06-1