- Code : #0809 10 mg
- Formula : C₃₀H₄₄O₉
- CAS : 508-77-0
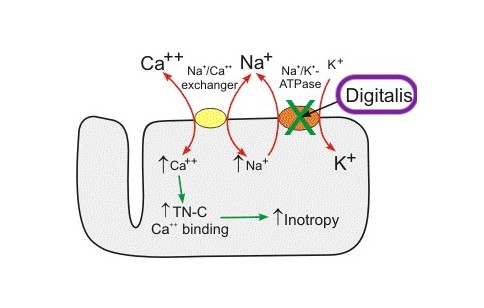
Cardiac glycoside
Cardiac glycosides and their aglycones (rarely called Cardanolides, their actual chemical class) are a group of naturally occurring steroid-like compounds found in various plants, particularly in the milkweed family (Asclepiadaceae), in foxglove and oleander. They are spreaded into two main subclasses : Cardenolides (with a C5 lactonic side chain « enolide ») and Bufadienolides (with a C6 lactonic side chain « dienolide »). These compounds are known for their ability to strengthen heart muscle contractions and are commonly used in the treatment of heart failure. However, they are primarily known for their role as defensive compounds in plants, serving to deter herbivores and parasites. Some cardenolides have also been shown to have cytotoxic properties and are being studied for potential use in cancer treatment.
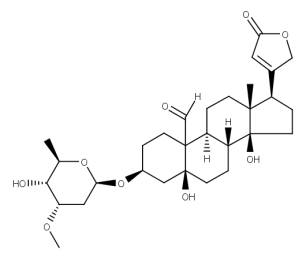
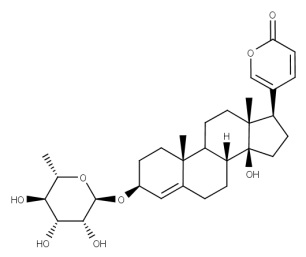
- Code : #0820 10 mg
- Formula : C₂₃H₃₄O₄
- CAS : 143-62-4
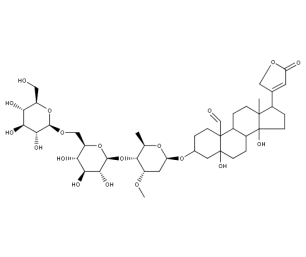
- Code : #0814 S 20 mg
- Formula : C₄₁H₆₄O₁₃
- CAS : 71-63-6
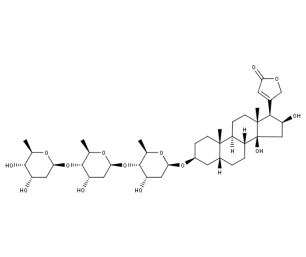
- Code : #0830 20 mg
- Formula : C₄₁H₆₄O₁₄
- CAS : 20830-75-5
- Code : #0823 S 5 mg
- Formula : C₄₁H₆₄O₁₄
- CAS : 4562-36-1
- Code : #0858 10 mg
- Formula : C₄₂H₆₄O₁₉
- CAS : 33279-57-1
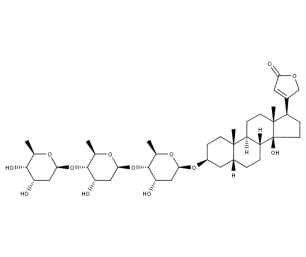
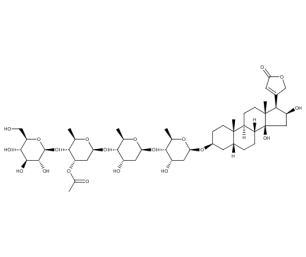
- Code : #0816 5 mg
- Formula : C₄₉H₇₆O₂₀
- CAS : 17575-21-2
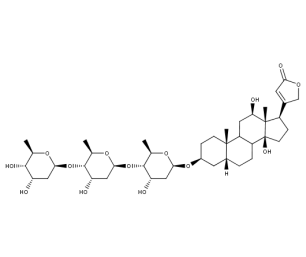
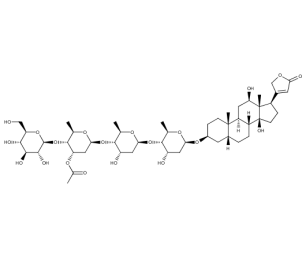
- Code : #0817 10 mg
- Formula : C₄₉H₇₆O₂₀
- CAS : 17575-22-3
- Code : #0852 10 mg
- Formula : C₃₀H₄₂O₈
- CAS : 466-06-8