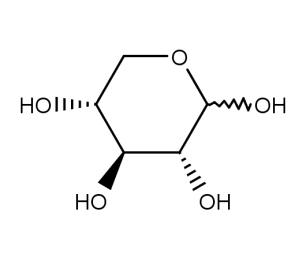
- Code : #4045 A 100 mg
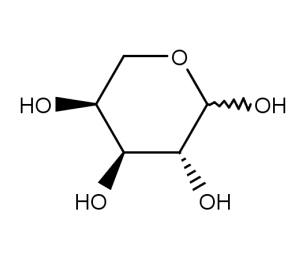
- Formula : C₅H₁₀O₅
- CAS : 5328-37-0
Plantago ovata
Plantago ovata, “Blond plantain” or “Blond psyllium” in English and “Psyllium blond” or “Ispaghul” in French, belongs to the Plantaginaceae botanical family.
Native to North African deserts, south-west Asia and south-west USA, it is a herb with a rosette of leaves 15cm long and a spike usually 9 cm tall carrying the flowers. It grows in deserts and dry open places, in margins of fields or grasslands.
Psyllium seeds have been used as medicinal agent since ancient times in European, Chinese and Ayurvedic medicine for the treatment of constipation, diarrhea, and irritable bowel syndrome, inflammatory bowel disease, colon cancer, diabetes, and hypercholesterolemia. It was also used to treat skin irritations such as poison ivy reactions and insect bites.
Among its main constituents are 20 to 30 % mucilage with up to 85 % weakly acidic arabinoxylans with a small proportion of rhamnose and galacturonic acid. The seeds contain fixed oil, protein, and very small amounts of iridoids, such as aucubin.

- Code : #0227 S 20 mg
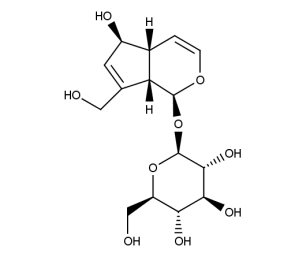
- Formula : C₁₅H₂₂O₉
- CAS : 479-98-1
- Code : #0233 S 10 mg
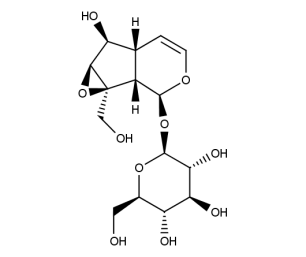
- Formula : C₁₅H₂₂O₁₀
- CAS : 2415-24-9
- Code : #4117 A 100 mg
- Formula : C₆H₁₂O₆
- CAS : 59-23-4
- Code : #4994 S 10 mg
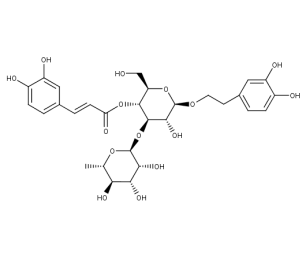
- Formula : C₂₉H₃₆O₁₅
- CAS : 61276-17-3
- Code : #4312 A 100 mg
- Formula : C₅H₁₀O₅
- CAS : 58-86-6